|
|
| Visit this group |
Archives
- passive or active
- analog or digital
- high-pass, low-pass, bandpass, band-reject (band reject; notch), or all-pass.
- discrete-time (sampled) or continuous-time
- linear or non-linear
- infinite impulse response (IIR type) or finite impulse response (FIR type)
History
The oldest forms of electronic filters are passive analog linear filters, constructed using only resistors and capacitors or resistors and inductors. These are known as RC and RL single-pole filters respectively. More complex multipole LC filters have also existed for many years, and their operation is well understood.Hybrid filters are also possible, typically involving a combination of analog amplifiers with mechanical resonators or delay lines. Other devices such as CCD delay lines have also been used as discrete-time filters. With the availability of digital signal processing, active digital filters have become common.
Classification by technology
Passive filters
Passive implementations of linear filters are based on combinations of resistors (R), inductors (L) and capacitors (C). These types are collectively known as passive filters, because they do not depend upon an external power supply and/or they do not contain active components such as transistors.Inductors block high-frequency signals and conduct low-frequency signals, while capacitors do the reverse. A filter in which the signal passes through an inductor, or in which a capacitor provides a path to ground, presents less attenuation to low-frequency signals than high-frequency signals and is a low-pass filter. If the signal passes through a capacitor, or has a path to ground through an inductor, then the filter presents less attenuation to high-frequency signals than low-frequency signals and is a high-pass filter. Resistors on their own have no frequency-selective properties, but are added to inductors and capacitors to determine the time-constants of the circuit, and therefore the frequencies to which it responds.
The inductors and capacitors are the reactive elements of the filter. The number of elements determines the order of the filter. In this context, an LC tuned circuit being used in a band-pass or band-stop filter is considered a single element even though it consists of two components.
At high frequencies (above about 100 megahertz), sometimes the inductors consist of single loops or strips of sheet metal, and the capacitors consist of adjacent strips of metal. These inductive or capacitive pieces of metal are called stubs.
Single element types

The quality or "Q" factor is a measure that is sometimes used to describe simple band-pass or band-stop filters. A filter is said to have a high Q if it selects or rejects a range of frequencies that is narrow in comparison to the centre frequency. Q may be defined for bandpass and band-reject filters as the ratio of centre frequency divided by 3dB bandwidth. It is not commonly employed with higher order filters where other parameters are of more concern, and for high-pass or low-pass filters Q is not normally related to bandwidth.
.
L filter
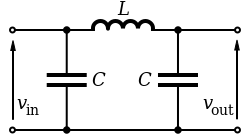
An L filter consists of two reactive elements, one in series and one in parallel.T and π filters
Three-element filters can have a 'T' or 'π' topology and in either geometries, a low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, or band-stop characteristic is possible. The components can be chosen symmetric or not, depending on the required frequency characteristics. The high-pass T filter in the illustration, has a very low impedance at high frequencies, and a very high impedance at low frequencies. That means that it can be inserted in a transmission line, resulting in the high frequencies being passed and low frequencies being reflected. Likewise, for the illustrated low-pass π filter, the circuit can be connected to a transmission line, transmitting low frequencies and reflecting high frequencies. Using m-derived filter sections with correct termination impedances, the input impedance can be reasonably constant in the pass bandMultiple element types
Multiple element filters are usually constructed as a ladder network. These can be seen as a continuation of the L,T and π designs of filters. More elements are needed when it is desired to improve some parameter of the filter such as stop-band rejection or slope of transition from pass-band to stop-band.Active filters
Active filters are implemented using a combination of passive and active (amplifying) components, and require an outside power source. Operational amplifiers are frequently used in active filter designs. These can have high Q, and can achieve resonance without the use of inductors. However, their upper frequency limit is limited by the bandwidth of the amplifiers used.Digital filters
Digital signal processing allows the inexpensive construction of a wide variety of filters. The signal is sampled and an analog to digital converter turns the signal into a stream of numbers. A computer program running on a CPU or a specialized DSP (or less often running on a hardware implementation of the algorithm) calculates an output number stream. This output can be converted to a signal by passing it through a digital to analog converter. There are problems with noise introduced by the conversions, but these can be controlled and limited for many useful filters. Due to the sampling involved, the input signal must be of limited frequency content or aliasing will occur.Other filter technologies
Quartz filters and piezoelectrics
In the late 1930s, engineers realized that small mechanical systems made of rigid materials such as quartz would acoustically resonate at radio frequencies, i.e. from audible frequencies (sound) up to several hundred megahertz. Some early resonators were made of steel, but quartz quickly became favored. The biggest advantage of quartz is that it is piezoelectric. This means that quartz resonators can directly convert their own mechanical motion into electrical signals. Quartz also has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion which means that quartz resonators can produce stable frequencies over a wide temperature range. Quartz crystal filters have much higher quality factors than LCR filters. When higher stabilities are required, the crystals and their driving circuits may be mounted in a "crystal oven" to control the temperature. For very narrow band filters, sometimes several crystals are operated in series.Engineers realized that a large number of crystals could be collapsed into a single component, by mounting comb-shaped evaporations of metal on a quartz crystal. In this scheme, a "tapped delay line" reinforces the desired frequencies as the sound waves flow across the surface of the quartz crystal. The tapped delay line has become a general scheme of making high-Q filters in many different way
SAW filters
SAW (surface acoustic wave) filters are electromechanical devices commonly used in radio frequency applications. Electrical signals are converted to a mechanical wave in a device constructed of a piezoelectric crystal or ceramic; this wave is delayed as it propagates across the device, before being converted back to an electrical signal by further electrodes. The delayed outputs are recombined to produce a direct analog implementation of a finite impulse response filter. This hybrid filtering technique is also found in an analog sampled filter. SAW filters are limited to frequencies up to 3 GHz.BAW filters
BAW (Bulk Acoustic Wave) filters are electromechanical devices. BAW filters can implement ladder or lattice filters. BAW filters typically operate at frequencies from around 2 to around 16 GHz, and in may be smaller or thinner than equivalent SAW filters. Two main variants of BAW filters are making their way into devices, Thin film bulk acoustic resonator or FBAR and Solid Mounted Bulk Acoustic Resonators.Garnet filters
Another method of filtering, at microwave frequencies from 800 MHz to about 5 GHz, is to use a synthetic single crystal yttrium iron garnet sphere made of a chemical combination of yttrium and iron (YIGF, or yttrium iron garnet filter). The garnet sits on a strip of metal driven by a transistor, and a small loop antenna touches the top of the sphere. An electromagnet changes the frequency that the garnet will pass. The advantage of this method is that the garnet can be tuned over a very wide frequency by varying the strength of the magnetic field.Atomic filters
For even higher frequencies and greater precision, the vibrations of atoms must be used. Atomic clocks use caesium masers as ultra-high Q filters to stabilize their primary oscillators. Another method, used at high, fixed frequencies with very weak radio signals, is to use a ruby maser tapped delay line.A device which performs the opposite function (converting DC to AC) is known as an inverter.
When only one diode is used to rectify AC (by blocking the negative or positive portion of the waveform), the difference between the term diode and the term rectifier is merely one of usage, i.e., the term rectifier describes a diode that is being used to convert AC to DC. Almost all rectifiers comprise a number of diodes in a specific arrangement for more efficiently converting AC to DC than is possible with only one diode. Before the development of silicon semiconductor rectifiers, vacuum tube diodes and copper(I) oxide or selenium rectifier stacks were used.
Early radio receivers, called crystal radios, used a "cat's whisker" of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena (lead sulfide) to serve as a point-contact rectifier or "crystal detector". Rectification may occasionally serve in roles other than to generate D.C. current per se. For example, in gas heating systems flame rectification is used to detect presence of flame. Two metal electrodes in the outer layer of the flame provide a current path, and rectification of an applied alternating voltage will happen in the plasma, but only while the flame is present to generate it.
Peak loss
An aspect of most rectification is a loss from peak input voltage to the peak output voltage, caused by the built-in voltage drop across the diodes (around 0.7 V for ordinary silicon p-n-junction diodes and 0.3 V for Schottky diodes). Half-wave rectification and full-wave rectification using two separate secondaries will have a peak voltage loss of one diode drop. Bridge rectification will have a loss of two diode drops. This may represent significant power loss in very low voltage supplies. In addition, the diodes will not conduct below this voltage, so the circuit is only passing current through for a portion of each half-cycle, causing short segments of zero voltage to appear between each "hump".Applications
The primary application of rectifiers is to derive DC power from an AC supply. Virtually all electronic devices require DC, so rectifiers find uses inside the power supplies of virtually all electronic equipment.Converting DC power from one voltage to another is much more complicated. One method of DC-to-DC conversion first converts power to AC (using a device called an inverter), then use a transformer to change the voltage, and finally rectifies power back to DC.
Rectifiers also find a use in detection of amplitude modulated radio signals. The signal may or may not be amplified before detection but if un-amplified a very low voltage drop diode must be used. When using a rectifier for demodulation the capacitor and load resistance must be carefully matched. Too low a capacitance will result in the high frequency carrier passing to the output and too high will result in the capacitor just charging and staying charged.
Rectifiers are also used to supply polarised voltage for welding. In such circuits control of the output current is required and this is sometimes achieved by replacing some of the diodes in bridge rectifier with thyristors, whose voltage output can be regulated by means of phase fired controllers.
Basic Principle
Construction:
Fluidomat fluid couplings work on the hydrodynamic principle. It consists of a pump-generally known as impeller and a turbine generally known as rotor, both enclosed suitably in a casing. The impeller and the rotor are bowl-shaped and have large number of radial vanes. They face each other with an air gap. The impeller is suitably connected to the prime mover while the rotor has a shaft bolted to it. This shaft is further connected to the driven machine through a suitable arrangement. Oil is filled in the fluid coupling from the filling plug provided on its body. A fusible plug is provided on the fluid coupling which blows off and drains out oil from the coupling in case of sustained overloading.
Operating Principle:
There is no mechanical interconnection between the impeller and the rotor (i.e. the driving and driven units) and the power is transmitted by virtue of the fluid filled in the coupling. The impeller when rotated by the prime mover imparts velocity and energy to the fluid, which is converted into mechanical energy in the rotor thus rotating it.
The fluid follows a closed circuit of flow from impeller to rotor through the air gap at the outer periphery and from rotor to impeller again through the air gap at the inner periphery. To enable the fluid to flow from impeller to rotor it is essential that there is difference in the "head" between the two and thus it is essential that there is difference in R.P.M., known as slip between the two. Slip is an important and inherent characteristic of a fluid coupling resulting in several desired advantages. As the slip increases more and more fluid can be transferred from the impeller to the rotor and more torque is transmitted. However when the rotor is at standstill, maximum fluid is transmitted from the coupling. The maximum torque is limiting torque. The fluid coupling also acts as a torque limiter.
Characteristics: Fluidomat fluid coupling has centrifugal characteristics during starting, thus enabling no load start-up of prime mover, which is of great importance. The slipping characteristics of fluid coupling provides a wide range of choice of power transmission characteristics which also result in speed variation, smooth & controlled acceleration, clutching and declutching operations and other characteristics of load limiting shock & peak load absorption and dampening etc. By varying the quantity of oil filled in the fluid coupling, the normal torque transmitting capacity can be varied. The maximum torque of the fluid coupling can also be set to a pre-determined safe value by adjusting the oil filling. The fluid coupling has the same characteristics in both directions of rotation.
Scoop Control Variable Speed Couplings :
These coupling have a sliding scoop tube which enters the coupling rotating casing through central clearance. The oil quantity level in the coupling can be varied which in operation by changing the position of the scoop tube which determines the oil level in the coupling. This change of oil level shifts the torque characteristic of the coupling thus enabling step less speed control .See the characteristic curve shown below.
Important Oil Properties:
Kinematic viscosity : 40 Deg.
Viscosity Index : 95
Flash Point : 190 Deg.
| Equivalent Oils: | |||
| IOC | SERVO SYSTEM 32 | ESSO | TORQUE FLUID N45 |
| BP | ENERGOL HLP 32 | GULF | HYDRAULIC OIL 32 |
| CALTEX | TORQUE FLUID 32 | SHELL | TOGULA OIL 32 |
| CASTROL | HYPSIN AWS 32 | MOBIL | MOBIL FLUID 124 |
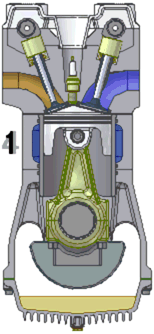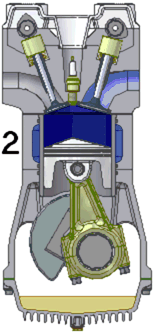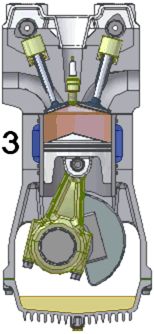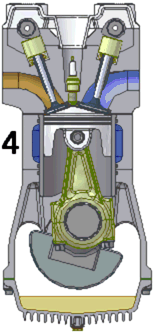
A petrol engine (known as a gasoline engine in North America) is an internal combustion engine with spark-ignition, designed to run on petrol (gasoline) and similar volatile fuels.
It differs from a diesel engine in the method of mixing the fuel and air, and in the fact that it uses spark plugs to initiate the combustion process. In a diesel engine, only air is compressed (and therefore heated), and the fuel is injected into the now very hot air at the end of the compression stroke, and self-ignites. In a petrol engine, the fuel and air are usually pre-mixed before compression (although some modern petrol engines now utilise cylinder-direct petrol injection). The pre-mixing was formerly done in a carburetor, but now (except in the smallest engines) it is done by electronically-controlled fuel injection. Pre-mixing of fuel and air allows a petrol engine to run at a much higher speed than a diesel, but severely limits their compression, and thus efficiency
The first fast-running petrol engine was invented by the German automobile pioneer Gottlieb Daimler.
Applications
Petrol engines have many applications, including:
- Motor cars
- Motorcycles
- Aircraft
- Motorboats
- Small machines, such as lawn mowers, chainsaws and portable engine-generators
Design
Working cycles
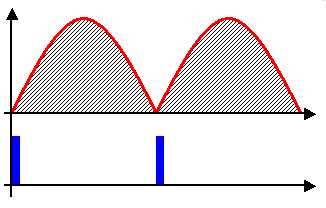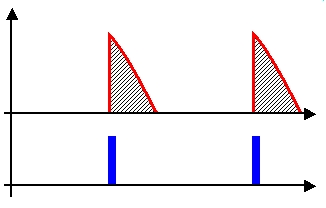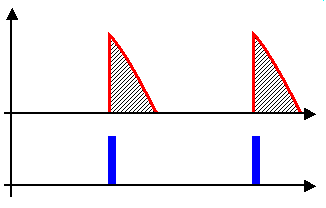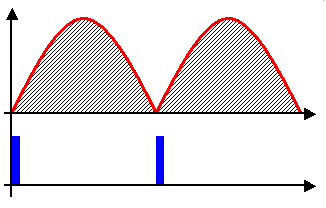
Petrol engines may run on the four-stroke cycle or the two-stroke cycle. For details of working cycles see:
Cylinder arrangement
Common cylinder arrangements are from 1 to 6 cylinders in-line or from 2 to 16 cylinders in V-formation. Flat engines -- like a V design flattened out-- are common in small airplanes and motorcycles and were a hallmark of Volkswagen automobiles into the 1990s. Flat 6s are still used in many modern Porsches, as well as Suburus. Many flat engines are air-cooled. Less common, but notable in vehicles designed for high speeds is the W formation, similar to having 2 V engines side by side. Alternatives include rotary and radial engines the latter typically have 7 or 9 cylinders in a single ring, or 10 or 14 cylinders in two rings.
Cooling
Petrol engines may be air-cooled, with fins (to increase the surface area on the cylinders) and cylinder head; or liquid-cooled, by a water jacket and radiator. The coolant was formerly water, but is now usually a mixture of water and ethylene glycol. This mixture has a lower freezing-point and a higher boiling-point than pure water, and also prevents corrosion, with modern antifreezes also containing lubricants and other additives to protect water pump seals and bearings. The cooling system is usually slightly pressurised to raise the boiling point of the coolant.
Compression ratio
The compression ratio is the ratio between the total volumes of the cylinder AND the combustion chambers - at the beginning, and end of the compression stroke. Broadly speaking, the higher the compression ratio, the higher the efficiency of the engine. However, compression ratio has to be limited to avoid pre-ignition of the fuel-air mixture which would cause engine knocking and damage to the engine. Modern motor-car engine generally have compression ratios of between 9:1 and 10:1, but this can go up to 11 or 12:1 for high-performance engines that run on higher octane fuel.
Ignition
Petrol engines use spark ignition and high voltage current for the spark may be provided by a magneto or an ignition coil. In modern car engines the ignition timing is managed by an electronic Engine Control UnitHow diesel engines work
The diesel internal combustion engine differs from the gasoline powered Otto cycle by using a higher compression of the air to ignite the fuel rather than using a spark plug ("compression ignition" rather than "spark ignition").
In the diesel engine, only air is introduced into the combustion chamber. The air is then compressed with a compression ratio typically between 15 and 22 resulting into a 40 bar (about 600 psi) pressure compared to 8 to 14 bar (about 200 psi) in the gasoline engine. This high compression heats the air to 550 °C (about 1000 °F). At about this moment (the exact moment is determined by the fuel injection timing of the fuel system), fuel is injected directly into the compressed air in the combustion chamber. This may be into a (typically toroidal) void in the top of the piston or a 'pre-chamber' depending upon the design of the engine. The fuel injector ensures that the fuel is broken down into small droplets, and that the fuel is distributed as evenly as possible. The more modern the engine, the smaller, more numerous and better distributed are the droplets. The heat of the compressed air vaporises fuel from the surface of the droplets. The vapour is then ignited by the heat from the compressed air in the combustion chamber, the droplets continue to vaporise from their surfaces and burn, getting smaller, until all the fuel in the droplets has been burnt. The start of vaporisation causes a delay period during ignition, and the characteristic diesel knocking sound as the vapour reaches ignition temperature and causes an abrupt increase in pressure above the piston. The rapid expansion of combustion gases then drives the piston downward, supplying power to the crankshaft.
As well as the high level of compression allowing combustion to take place without a separate ignition system, a high compression ratio greatly increases the engine's efficiency. Increasing the compression ratio in a spark-ignition engine where fuel and air are mixed before entry to the cylinder is limited by the need to prevent damaging pre-ignition. Since only air is compressed in a diesel engine, and fuel is not introduced into the cylinder until shortly before top dead center (TDC), premature detonation is not an issue and compression ratios are much higher.
Early fuel injection systems
Diesel's original engine injected fuel with the assistance of compressed air, which atomized the fuel and forced it into the engine through a nozzle (a similar principle to an aerosol spray). The nozzle opening was closed by a pin valve lifted by the camshaft to initiate the fuel injection before top dead center (TDC). This is called an air-blast injection. Driving the three stage compressor used some power but the efficiency and net power output was more than any other combustion engine at that time. Diesel engines in service today raise the fuel to extreme pressures by mechanical pumps and deliver it to the combustion chamber by pressure-activated injectors without compressed air. With direct injected diesels, injectors spray fuel through six or more small orifices in its nozzle. The early air injection diesels always had a superior combustion without the sharp increase in pressure during combustion. Interestingly research is performed and patents are taken out to use some form of air injection to reduce the nitrogen oxides and pollution, reverting to Diesels original implementation with its superior combustion. In all major aspects, it holds true to Rudolf Diesel's original design, that of igniting fuel by compression at an extremely high pressure within the cylinder. With much higher pressures and high technology injectors present-day diesel engines use the so-called solid injection system applied by Herbert Akroyd Stuart for his hot bulb engine. The indirect injection engine could be considered the latest development of these low speed "hot bulb" ignition engines
Cold weather
Starting
In cold weather, high speed diesel engines, which are mostly prechambered, can be difficult to start because the mass of the cylinder block and cylinder head absorb the heat of compression, preventing ignition because of the higher surface to volume ratio. Prechambered engines therefore make use of small electric heaters inside the prechambers called glowplugs. These engines also generally have a higher compression ratio of 19:1 to 21:1. Low speed and compressed air started larger and intermediate speed diesels do not have glowplugs and compression ratios are around 16:1. Some engines use resistive grid heaters in the intake manifold to warm the inlet air until the engine reaches operating temperature. Engine block heaters (electric resistive heaters in the engine block) connected to the utility grid are often used when an engine is turned off for extended periods (more than an hour) in cold weather to reduce startup time and engine wear. In the past, a wider variety of cold-start methods were used. Some engines, such as Detroit Diesel engines and Lister-Petter engines, used a system to introduce small amounts of ether into the inlet manifold to start combustion. Saab marine engines, Field Marshall tractors (among others) used slow-burning solid-fuel 'cigarettes' which were fitted into the cylinder head as a primitive glow plug. Lucas developed the 'Thermostart', where an electrical heating element was combined with a small fuel valve. Diesel fuel slowly dripped from the valve onto the hot element and ignited. The flame heated the inlet manifold and when the engine was turned over the flame was drawn into the combustion chamber to start combustion. International Harvester developed a WD-40 tractor in the 1930s that had a 7-liter 4-cylinder engine which ran as a diesel, but was started as a gasoline engine. The cylinder head had valves which opened for a portion of the compression stroke to reduce the effective compression ratio, and a magneto produced the spark. An automatic ratchet system automatically disengaged the ignition system and closed the valves once the engine had run for 30 seconds. The operator then switched off the gasoline fuel system and opened the throttle on the diesel injection system. Recently direct-injection systems advanced to the extent that prechambers systems were not needed using a common rail with electronic fuel injection.
Gelling
Diesel fuel is also prone to "waxing" or "gelling" in cold weather, terms for the solidification of diesel oil into a partially crystalline state. The crystals build up in the fuel line (especially in fuel filters), eventually starving the engine of fuel and causing it to stop running. Low-output electric heaters in fuel tanks and around fuel lines are used to solve this problem. Also, most engines have a "spill return" system, by which any excess fuel from the injector pump and injectors is returned to the fuel tank. Once the engine has warmed, returning warm fuel prevents waxing in the tank. Due to improvements in fuel technology, with additives waxing rarely occurs in all but the coldest weather when a mix of diesel and kerosene should be used to run a vehicle.
Fuel delivery
A vital component of all diesel engines is a mechanical or electronic governor which regulates the idling speed and maximum speed of the engine by controlling the rate of fuel delivery. Unlike Otto-cycle engines, incoming air is not throttled and a diesel engine without a governor can not have a stable idling speed and can easily overspeed, resulting in its destruction. Mechanically governed fuel injection systems are driven by the engine's gear train.These systems use a combination of springs and weights to control fuel delivery relative to both load and speed. Modern, electronically controlled diesel engines control fuel delivery by use of an electronic control module (ECM) or electronic control unit (ECU). The ECM/ECU receives an engine speed signal, as well as other operating parameters such as intake manifold pressure and fuel temperature, from a sensor and controls the amount of fuel and start of injection timing through actuators to maximize power and efficiency and minimize emissions. Controlling the timing of the start of injection of fuel into the cylinder is a key to minimizing emissions, and maximizing fuel economy (efficiency), of the engine. The timing is measured in degrees of crank angle of the piston before top dead center. For example, if the ECM/ECU initiates fuel injection when the piston is 10 degrees before TDC, the start of injection, or timing, is said to be 10° BTDC. Optimal timing will depend on the engine design as well as its speed and load. Advancing the start of injection (injecting before the piston reaches TDC) results in higher in-cylinder pressure and temperature, and higher efficiency, but also results in elevated engine noise and increased oxides of nitrogen (NOx) emissions due to higher combustion temperatures. Delaying start of injection causes incomplete combustion, reduced fuel efficiency and an increase in exhaust smoke, containing a considerable amount of particulate matter and unburned hydrocarbons .Mechanical and electronic injection
Many configurations of fuel injection have been used over the past century (1900–2000).
Most present day (2008) diesel engines make use of a camshaft, rotating at half crankshaft speed, lifted mechanical single plunger high pressure fuel pump driven by the engine crankshaft. For each cylinder, its plunger measures the amount of fuel and determines the timing of each injection. These engines use injectors that are basically very precise spring-loaded valves that open and close at a specific fuel pressure. For each cylinder a plunger pump is connected with an injector with a high pressure fuel line. Fuel volume for each single combustion is controlled by a slanted groove in the plunger which rotates only a few degrees releasing the pressure and is controlled by a mechanical governor, consisting of weights rotating at engine speed constrained by springs and a lever. The injectors are held open by the fuel pressure. On high speed engines the plunger pumps are together in one unit
Each fuel line should have the same length to obtain the same pressure delay. A cheaper configuration on high speed engines with less than six cylinders is to use an axial-piston distributor pump ,consisting of one rotating pump plunger delivering fuel to a valve and line for each cylinder (functionally analogous to points and distributor cap on an Otto engine).This contrasts with the more modern method of having a single fuel pump which supplies fuel constantly at high pressure with a common rail (single fuel line common) to each injector. Each injector has a solenoid operated by an electronic control unit, resulting in more accurate control of injector opening times that depend on other control conditions, such as engine speed and loading, and providing better engine performance and fuel economy. This design is also mechanically simpler than the combined pump and valve design, making it generally more reliable, and less noisy, than its mechanical counterpart.
Both mechanical and electronic injection systems can be used in either direct or indirect injection configurations.
Older diesel engines with mechanical injection pumps could be inadvertently run in reverse, albeit very inefficiently, as witnessed by massive amounts of soot being ejected from the air intake. This was often a consequence of push starting a vehicle using the wrong gear. Large ship diesels can run either way.
Indirect injection
An indirect injection diesel engine delivers fuel into a chamber off the combustion chamber, called a prechamber or ante-chamber, where combustion begins and then spreads into the main combustion chamber, assisted by turbulence created in the chamber. This system allows for a smoother, quieter running engine, and because combustion is assisted by turbulence, injector pressures can be lower, about 100 bar using a single orifice tapered jet injector . Mechanical injection systems allowed high-speed running suitable for road vehicles (typically up to speeds of around 4,000 rpm). The prechamber had the disadvantage of increasing heat loss to the engine's cooling system, and restricting the combustion burn, which reduced the efficiency by 5%–10%. Indirect injection engines were used in small-capacity, high-speed diesel engines in automotive, marine and construction uses from the 1950s, until direct injection technology advanced in the 1980s. Indirect injection engines are cheaper to build and it is easier to produce smooth, quiet-running vehicles with a simple mechanical system. In road-going vehicles most prefer the greater efficiency and better controlled emission levels of direct injection.Direct injection
Modern diesel engines make use of one of the following direct injection methods:
Direct injection injectors are mounted in the top of the combustion chamber. The problem with these vehicles was the harsh noise that they made. Fuel consumption was about 15 to 20 percent lower than indirect injection diesels, which for some buyers was enough to compensate for the extra noise.
This type of engine was transformed by electronic control of the injection pump, pioneered by the Volkswagen Group in 1989. The injection pressure was still only around 300 bar (4350 psi), but the injection timing, fuel quantity, EGR and turbo boost were all electronically controlled. This gave more precise control of these parameters which made refinement more acceptable and emissions lower.
Unit direct injection
Unit direct injection also injects fuel directly into the cylinder of the engine. In this system the injector and the pump are combined into one unit positioned over each cylinder controlled by the camshaft. Each cylinder has its own unit eliminating the high pressure fuel lines, achieving a more consistent injection. This type of injection system, also developed by Bosch, is used by Volkswagen AG in cars (where it is called a Pumpe-Düse-System—literally "pump-nozzle system") and by Mercedes Benz ("PLD") and most major diesel engine manufacturers in large commercial engines (CAT, Cummins, Detroit Diesel, Volvo). With recent advancements, the pump pressure has been raised to 2,400 bar (35261 psi) allowing injection parameters similar to common rail systems.Common rail direct injection
In common rail systems, the separate pulsing high pressure fuel line to each cylinder injector is also eliminated. Instead, a high-pressure pump pressurizes fuel at up to 2,000 bar (200 MPa, 30000 psi),in a "common rail". The common rail is a tube that supplies each computer-controlled injector containing a precision-machined nozzle and a plunger driven by a solenoid or piezoelectric actuator. TYPES:Early
Rudolf Diesel intended his engine to replace the steam engine as the primary power source for industry. As such, diesel engines in the late 19th and early 20th centuries used the same basic layout and form as industrial steam engines, with long-bore cylinders, external valve gear, cross-head bearings and an open crankshaft connected to a large flywheel. Smaller engines would be built with vertical cylinders, while most medium- and large-sized industrial engines were built with horizontal cylinders, just as steam engines had been. Engines could be built with more than one cylinder in both cases. The largest early diesels resembled the triple-expansion reciprocating engine steam engine, being tens of feet high with vertical cylinders arranged in-line. These early engines ran at very slow speeds—partly due to the limitations of their air-blast injector equipment and partly so they would be compatible with the majority of industrial equipment designed for steam engines; maximum speeds of between 100 and 300 rpm were common. Engines were usually started by allowing compressed air into the cylinders to turn the engine, although smaller engines could be started by hand.
crosshead bearing. Following steam engine practice some manufactures made double-acting two-stroke and four-stroke diesel engines to increase power output, with combustion taking place on both sides of the piston, with two sets of valve gear and fuel injection. While it produced large amounts of power and was very efficient, the double-acting diesel engine's main problem was producing a good seal where the piston rod passed through the bottom of the lower combustion chamber to the crosshead bearing, and no more were built. By the 1930s turbochargers were fitted to some engines. Crosshead bearings are still used to reduce the wear on the cylinders in large long-stroke main marine engines.
Modern
As with gasoline engines, there are two classes of diesel engines in current use: two-stroke and four-stroke. The four-stroke type is the "classic" version, tracing its lineage back to Rudolf Diesel's prototype. It is also the most commonly used form, being the preferred power source for many motor vehicles, especially buses and trucks. Much larger engines, such as used for railroad locomotion and marine propulsion, are often two-stroke units, offering a more favorable power-to-weight ratio, as well as better fuel economy. The most powerful engines in the world are two-stroke diesels of mammoth proportions.Two-stroke diesel operation is similar to that of gasoline counterparts, except that fuel is not mixed with air prior to induction, and the crankcase does not take an active role in the cycle. The traditional two-stroke design relies upon a mechanically driven positive displacement blower to charge the cylinders with air prior to compression and ignition. The charging process also assists in expelling (scavenging) combustion gases remaining from the previous power stroke. The archetype of the modern form of the two-stroke Diesel is the Detroit Diesel engine, in which the blower pressurizes a chamber in the engine block that is often referred to as the "air box". The (much larger) Electromotive prime mover utilized in EMD Diesel-electric locomotives is built to the same principle.
In a two-stroke diesel engine, as the cylinder's piston approaches the bottom dead center exhaust ports or valves are opened relieving most of the excess pressure after which a passage between the air box and the cylinder is opened, permitting air flow into the cylinder.
The air flow blows the remaining combustion gases from the cylinder—this is the scavenging process. As the piston passes through bottom center and starts upward, the passage is closed and compression commences, culminating in fuel injection and ignition. Refer to two-stroke Diesel engines for more detailed coverage of aspiration types and supercharging of two-stroke engine.
Normally, the number of cylinders are used in multiples of two, although any number of cylinders can be used as long as the load on the crankshaft is counterbalanced to prevent excessive vibration. The inline-six cylinder design is the most prolific in light to medium-duty engines, though small V8 and larger inline-four displacement engines are also common. Small-capacity engines (generally considered to be those below five litres in capacity) are generally four or six cylinder types, with the four cylinder being the most common type found in automotive uses. Five cylinder diesel engines have also been produced, being a compromise between the smooth running of the six cylinder and the space-efficient dimensions of the four cylinder. Diesel engines for smaller plant machinery, boats, tractors, generators and pumps may be four, three or two cylinder types, with the single cylinder diesel engine remaining for light stationary work. Direct reversible two-stroke marine diesels need at least three cylinders for reliable restarting forwards and reverse. Four-stroke engines need at least six cylinders, providing repeated power strokes at 120 degrees.
The desire to improve the diesel engine's power-to-weight ratio produced several novel cylinder arrangements to extract more power from a given capacity. The opposed piston engine uses two pistons in one cylinder with the combustion cavity in the middle and gas in- and outlets at the ends. This makes a comparatively light, powerful, swiftly running and economic engine suitable for use in aviation. An example is the Junkers Jumo 204/205. The Napier Deltic engine, with three cylinders arranged in a triangular formation, each containing two opposed-action pistons, the whole engine having three crankshafts, is one of the better known. The Commer van company of the United Kingdom used a similar design for road vehicles, designed by Tillings-Stevens, member of the Rootes Group, the TS3. The Commer TS3 engine had 3 horizontal in-line cylinders, each with two opposed action pistons that worked through rocker arms, to connecting rods and had one crankshaft. While both these designs succeeded in producing greater power for a given capacity, they were complex and expensive to produce and operate, and when turbocharger technology improved in the 1960s, this was found to be a much more reliable and simple way of extracting more power.
Gas generator
As a footnote, prior to 1950, Sulzer started experimenting with two-stroke engines with boost pressures as high as 6 atmospheres, in which all of the output power was taken from an exhaust gas turbine. The two-stroke pistons directly drove air compressor pistons to make a positive displacement gas generator. Opposed pistons were connected by linkages instead of crankshafts. Several of these units could be connected together to provide power gas to one large output turbine. The overall thermal efficiency was roughly twice that of a simple gas turbine.This system was derived from Raúl Pateras PescaraAdvantages and disadvantages versus spark-ignition engines:
Power and fuel economyThe MAN S80ME-C7 low speed diesel engines use 155 gram fuel per kWh for an overall energy conversion efficiency of 54.4%, which is the highest conversion of fuel into power by any internal or external combustion engine
Diesel engines are more efficient than gasoline (petrol) engines of the same power, resulting in lower fuel consumption. A common margin is 40% more miles per gallon for an efficient turbodiesel. For example, the current model Škoda Octavia, using Volkswagen Group engines, has a combined Euro rating of 6.2 L/100 km (38 miles per US gallon) for the 102 bhp (76 kW) petrol engine and 4.4 L/100 km (54 mpg) for the 105 bhp (78 kW) diesel engine. However, such a comparison doesn't take into account that diesel fuel is denser and contains about 15% more energy by volume. Although the calorific value of the fuel is slightly lower at 45.3 MJ/kg (megajoules per kilogram) than gasoline at 45.8 MJ/kg, liquid diesel fuel is significantly denser than liquid gasoline. This is important because volume of fuel, in addition to mass, is an important consideration in mobile applications. No vehicle has an unlimited volume available for fuel storage.
Adjusting the numbers to account for the energy density of diesel fuel, the overall energy efficiency is still about 20% greater for the diesel version.
While higher compression ratio is helpful in raising efficiency, diesel engines are much more efficient than gasoline (petrol) engines when at low power and at engine idle. Unlike the petrol engine, diesels lack a butterfly valve (throttle) in the inlet system, which closes at idle. This creates parasitic loss and destruction of availability on the incoming air, reducing the efficiency of petrol/gasoline engines at idle. In many applications, such as marine, agriculture, and railways, diesels are left idling unattended for many hours or sometimes days. These advantages are especially attractive in locomotives (see dieselisation).
Weight can be an issue, since diesel engines are typically heavier than gasoline engines of similar power output. This is essentially because the diesel must operate at lower engine speeds.
Diesel fuel is injected just before the power stroke. As a result of this, the fuel cannot burn completely until it has encountered the right amount of oxygen. This results in incomplete combustion with too much fuel, poor design or failing injectors resulting in black exhaust. In the gasoline engine, air and fuel are mixed for the entire compression stroke, ensuring complete mixing even at higher engine speeds.
Diesel engines usually have longer stroke lengths to achieve the necessary compression ratios. As a result piston and connecting rods are heavier and more force must be transmitted through the connecting rods and crankshaft to change the momentum of the piston. This is another reason that a diesel engine must be stronger for the same power output.
Yet it is this same build quality that has allowed some enthusiasts to acquire significant power increases with turbocharged engines through fairly simple and inexpensive modifications. A gasoline engine of similar size cannot put out a comparable power increase without extensive alterations because the stock components would not be able to withstand the higher stresses placed upon them. Since a diesel engine is already built to withstand higher levels of stress, it makes an ideal candidate for performance tuning with little expense. However, it should be said that any modification that raises the amount of fuel and air put through a diesel engine will increase its operating temperature which will reduce its life and increase service requirements. These are issues with newer, lighter, high performance diesel engines which are not "overbuilt" to the degree of older engines and are being pushed to provide greater power in smaller engines. The addition of a turbocharger or supercharger to the engine greatly assists in increasing fuel economy and power output, mitigating the fuel-air intake speed limit mentioned above for a given engine displacement. Boost pressures can be higher on diesels than gasoline engines, due to the latter's susceptibility to knock, and the higher compression ratio allows a diesel engine to be more efficient than a comparable spark ignition engine. Because the burned gases are expanded further in a diesel engine cylinder, the exhaust gas is cooler, meaning turbochargers require less cooling, and can be more reliable, than on spark-ignition engines.
With a diesel, boost pressure is essentially unlimited. It is literally possible to run as much boost as the engine will physically stand before breaking apart. Consequently, engine designers have come to realize that diesels are capable of substantially more power and torque than any comparably sized gasoline engine.
The increased fuel economy of the diesel engine over the gasoline engine means that the diesel produces less carbon dioxide (CO2) per unit distance. Recently, advances in production and changes in the political climate have increased the availability and awareness of biodiesel, an alternative to petroleum-derived diesel fuel with a much lower net-sum emission of CO2, due to the absorption of CO2 by plants used to produce the fuel. Although concerns are now being raised as to the negative effect this is having on the world food supply, as the growing of crops specifically for biofuels takes up land that could be used for food crops and uses water that could be used by both humans and animals. The use of waste vegetable oil, sawmill waste from managed forests in Finland funded by Nokia venture capital, and the development of the production of vegetable oil from algae, demonstrate great promise in providing feed stocks for sustainable biodiesel, that are not in competition with food production.
Diesel engines have lower power output than equivalent size petrol engine because its speed is limited by the time required for combustion.
A combination of improved mechanical technology (such as multi-stage injectors which fire a short "pilot charges" of fuel into the cylinder to warm the combustion chamber before delivering the main fuel charge), higher injection pressures that have improved the atomisation of fuel into smaller droplets, and electronic control (which can adjust the timing and length of the injection process to optimise it for all speeds and temperatures), have mostly mitigated these problems in the latest generation of common-rail designs, while greatly improving engine efficiency. Poor power and narrow torque bands have been addressed by the use of superchargers, turbochargers, (especially variable geometry turbochargers), intercoolers, and a large efficiency increase from about 35% for IDI to 45% for the latest engines in the last 15 years.
Even though diesel engines have a theoretical fuel efficiency of 75%, in practice it is less. Engines in large diesel trucks, buses, and newer diesel cars can achieve peak efficiencies around 45%,
and could reach 55% efficiency in the near future.However, average efficiency over a driving cycle is lower than peak efficiency. For example, it might be 37% for an engine with a peak efficiency of 44%.Emissions
Diesel engines produce very little carbon monoxide as they burn the fuel in excess air even at full load, at which point the quantity of fuel injected per cycle is still about 50% lean of stoichiometric. However, they can produce black soot (or more specifically diesel particulate matter) from their exhaust, which consists of unburned carbon compounds. This is caused by local low temperatures where the fuel is not fully atomized. These local low temperatures occur at the cylinder walls and at the outside of large droplets of fuel. At these areas where it is relatively cold, the mixture is rich (contrary to the overall mixture which is lean). The rich mixture has less air to burn and some of the fuel turns into a carbon deposit. Modern car engines use a diesel particulate filter (DPF) to capture carbon particles and then intermittently burn them using extra fuel injected into the engine.
The full load limit of a diesel engine in normal service is defined by the "black smoke limit". Beyond which point the fuel cannot be completely combusted, as the "black smoke limit" is still considerably lean of stoichiometric. It is possible to obtain more power by exceeding it, but the resultant inefficient combustion means that the extra power comes at the price of reduced combustion efficiency, high fuel consumption and dense clouds of smoke. This is only done in specialized applications (such as tractor pulling competitions) where these disadvantages are of little concern.
Likewise, when starting from cold, the engine's combustion efficiency is reduced because the cold engine block draws heat out of the cylinder in the compression stroke. The result is that fuel is not combusted fully, resulting in blue/white smoke and lower power outputs until the engine has warmed through. This is especially the case with indirect injection engines, which are less thermally efficient. With electronic injection, the timing and length of the injection sequence can be altered to compensate for this. Older engines with mechanical injection can have mechanical and hydraulic governor control to alter the timing, and multi-phase electrically controlled glow plugs, that stay on for a period after start-up to ensure clean combustion—the plugs are automatically switched to a lower power to prevent them burning out.
Particles of the size normally called PM10 (particles of 10 micrometres or smaller) have been implicated in health problems, especially in cities. Some modern diesel engines feature diesel particulate filters, which catch the black soot and when saturated are automatically regenerated by burning the particles. Other problems associated with the exhaust gases (nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides) can be mitigated with further investment and equipment; some diesel cars now have catalytic converters in the exhaust.
All diesel engine exhaust emissions can be significantly reduced by the use of biodiesel fuel. Oxides of nitrogen do increase from a vehicle using biodiesel, but they too can be reduced to levels below that of fossil fuel diesel, by changing fuel injection timing.
Power and torque
For commercial uses requiring towing, load carrying and other tractive tasks, diesel engines tend to have better torque characteristics. Diesel engines tend to have their torque peak quite low in their speed range (usually between 1600–2000 rpm for a small-capacity unit, lower for a larger engine used in a truck). This provides smoother control over heavy loads when starting from rest, and, crucially, allows the diesel engine to be given higher loads at low speeds than a gasoline engine, making them much more economical for these applications. This characteristic is not so desirable in private cars, so most modern diesels used in such vehicles use electronic control, variable geometry turbochargers and shorter piston strokes to achieve a wider spread of torque over the engine's speed range, typically peaking at around 2500–3000 rpm.Noise
The characteristic noise of a diesel engine is variably called diesel clatter, diesel nailing, or diesel knockDiesel clatter is caused largely by the diesel combustion process, the sudden ignition of the diesel fuel when injected into the combustion chamber causes a pressure wave. Engine designers can reduce diesel clatter through: indirect injection; pilot or pre-injection; injection timing; injection rate; compression ratio; turbo boost; and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR).Common rail diesel injection systems permit multiple pre-injections as an aid to noise reduction. Diesel fuels with a higher cetane rating modify the combustion process and reduce diesel clatter.CN (Cetane number) can be raised by distilling higher quality crude oil, or by using a cetane improving additive. Some oil companies market high cetane or premium diesel. Biodiesel has a higher cetane number than petrodiesel, typically 55CN for 100% biodiesel.A combination of improved mechanical technology such as multi-stage injectors which fire a short "pilot charges" of fuel into the cylinder to initiate combustion before delivering the main fuel charge, higher injection pressures that have improved the atomisation of fuel into smaller droplets, and electronic control (which can adjust the timing and length of the injection process to optimise it for all speeds and temperatures), have mostly mitigated these problems in the latest generation of common-rail designs, while improving engine efficiency.Reliability
The lack of an electrical ignition system greatly improves the reliability. The high durability of a diesel engine is also due to its overbuilt nature (see above), a benefit that is magnified by the lower rotating speeds in diesels. Diesel fuel is a better lubricant than gasoline so is less harmful to the oil film on piston rings and cylinder bores; it is routine for diesel engines to cover 250,000 miles (400,000 km) or more without a rebuild.
Due to the greater compression force required and the increased weight of the stronger components, starting a diesel engine is harder. More torque is required to push the engine through compression.
Either an electrical starter or an air start system is used to start the engine turning. On large engines, pre-lubrication and slow turning of an engine, as well as heating, are required to minimize the amount of engine damage during initial start-up and running. Some smaller military diesels can be started with an explosive cartridge, called a Coffman starter, which provides the extra power required to get the machine turning. In the past, Caterpillar and John Deere used a small gasoline pony motor in their tractors to start the primary diesel motor. The pony motor heated the diesel to aid in ignition and utilized a small clutch and transmission to actually spin up the diesel engine. Even more unusual was an International Harvester design in which the diesel motor had its own carburetor and ignition system, and started on gasoline. Once warmed up, the operator moved two levers to switch the motor to diesel operation, and work could begin. These engines had very complex cylinder heads, with their own gasoline combustion chambers, and in general were vulnerable to expensive damage if special care was not taken (especially in letting the engine cool before turning it off).
As mentioned above, diesel engines tend to have more torque at lower engine speeds than gasoline engines. However, diesel engines tend to have a narrower power band than gasoline engines. Naturally-aspirated diesels tend to lack power and torque at the top of their speed range. This narrow band is a reason why a vehicle such as a truck may have a gearbox with as many as 18 or more gears, to allow the engine's power to be used effectively at all speeds. Turbochargers tend to improve power at high engine speeds; superchargers improve power at lower speeds; and variable geometry turbochargers improve the engine's performance equally by flattening the torque curve.
Quality and variety of fuels
Petrol/gasoline engines are limited in the variety and quality of the fuels they can burn. Older petrol engines fitted with a carburetor required a volatile fuel that would vaporize easily to create the necessary fuel/air mix for combustion. Because both air and fuel are admitted to the cylinder, if the compression ratio of the engine is too high or the fuel too volatile (with too low an octane rating), the fuel will ignite under compression, as in a diesel engine, before the piston reaches the top of its stroke. This pre-ignition causes a power loss and over time major damage to the piston and cylinder. The need for a fuel that is volatile enough to vaporize but not too volatile (to avoid pre-ignition) means that petrol engines will only run on a narrow range of fuels. There has been some success at dual-fuel engines that use gasoline/ethanol, gasoline/propane, and gasoline/methane.
In diesel engines, a mechanical injector system vaporizes the fuel into a pre-combustion chamber (as opposed to a Venturi jet in a carburetor, or a Fuel injector in a fuel injection system vaporizing fuel into the intake manifold or intake runners as in a petrol engine). This forced vaporisation means that less-volatile fuels can be used. More crucially, because only air is inducted into the cylinder in a diesel engine, the compression ratio can be much higher as there is no risk of pre-ignition provided the injection process is accurately timed. This means that cylinder temperatures are much higher in a diesel engine than a petrol engine, allowing less volatile fuels to be used.
Diesel fuel is a form of light fuel oil, very similar to kerosene, but diesel engines, especially older or simple designs that lack precision electronic injection systems, can run on a wide variety of other fuels. Some of the most common alternatives are Jet A-1 or vegetable oil from a very wide variety of plants. Some engines can be run on vegetable oil without modification, and most others require fairly basic alterations. Biodiesel is a pure diesel-like fuel refined from vegetable oil and can be used in nearly all diesel engines. The only limits on the fuels used in diesel engines are the ability of the fuel to flow along the fuel lines and the ability of the fuel to lubricate the injector pump and injectors adequately. In general terms, inline mechanical injector pumps tolerate poor-quality or bio-fuels better than distributor-type pumps. Also, indirect injection engines generally run more satisfactorily on bio-fuels than direct injection engines. This is partly because an indirect injection engine has a much greater 'swirl' effect, improving vaporisation and combustion of fuel, and also because (in the case of vegetable oil-type fuels) lipid depositions can condense on the cylinder walls of a direct-injection engine if combustion temperatures are too low (such as starting the engine from cold).
At the request of the French Government the Otto company demonstrated a diesel engine at the 1900 Exposition Universelle (World's Fair) which used peanut oil (see biodiesel). The French government were at the time exploring the possibility of using peanut oil as a locally produced fuel in their African colonies. Diesel himself later tested extensively the use of plant oils in his engine and began to actively promote the use of these fuels.
Most large marine diesels (often called cathedral engines due to their size) run on heavy fuel oil (sometimes called "bunker oil"), which is a thick, viscous and almost un-flammable fuel which is very safe to store and cheap to buy in bulk as it is a waste product from the petroleum refining industry. The fuel must be heated to thin it out (often by the exhaust header) and is often passed through multiple injection stages to vaporize it.
Fuel and fluid characteristics
Diesel engines can operate on a variety of different fuels, depending on configuration, though the eponymous diesel fuel derived from crude oil is most common. The engines can work with the full spectrum of crude oil distillates, from natural gas, alcohols, gasoline, wood gas to the fuel oils from diesel oil to residual fuels.The type of fuel used is a combination of service requirements, and fuel costs. Good-quality diesel fuel can be synthesised from vegetable oil and alcohol. Diesel fuel can be made from coal or other carbon base using the Fischer-Tropsch process. Biodiesel is growing in popularity since it can frequently be used in unmodified engines, though production remains limited. Recently, biodiesel from coconut, which can produce a very promising coco methyl esther (CME), has characteristics which enhance lubricity and combustion giving a regular diesel engine without any modification more power, less particulate matter or black smoke, and smoother engine performance. The Philippines pioneers in the research on Coconut based CME with the help of German and American scientists. Petroleum-derived diesel is often called petrodiesel if there is need to distinguish the source of the fuel.
Pure plant oils are increasingly being used as a fuel for cars, trucks and remote combined heat and power generation especially in Germany where hundreds of decentralised small- and medium-sized oil presses cold press oilseed, mainly rapeseed, for fuel. There is a Deutsches Institut für Normung fuel standard for rapeseed oil fuel.
Residual fuels are the "dregs" of the distillation process and are a thicker, heavier oil, or oil with higher viscosity, which are so thick that they are not readily pumpable unless heated. Residual fuel oils are cheaper than clean, refined diesel oil, although they are dirtier. Their main considerations are for use in ships and very large generation sets, due to the cost of the large volume of fuel consumed, frequently amounting to many tonnes per hour. The poorly refined biofuels straight vegetable oil (SVO) and waste vegetable oil (WVO) can fall into this category, but can be viable fuels on non common rail or TDI PD diesels with the simple conversion of fuel heating to 80 to 100 degrees Celsius to reduce viscosity, and adequate filtration to OEM standards. Engines using these heavy oils have to start and shut down on standard diesel fuel ,as these fuels will not flow through fuel lines at low temperatures. Moving beyond that, use of low-grade fuels can lead to serious maintenance problems because of their high sulfur content. Most diesel engines that power ships like supertankers are built so that the engine can safely use low-grade fuels due to their separate cylinder and crankcase lubrication.
Normal diesel fuel is more difficult to ignite and slower in developing fire than gasoline because of its higher flash point, but once burning, a diesel fire can be fierce.
Fuel contaminants such as dirt and water are often more problematic in diesel engines than in gasoline engines. Water can cause serious damage, due to corrosion, to the injection pump and injectors; and dirt, even very fine particulate matter, can damage the injection pumps due to the close tolerances that the pumps are machined to. All diesel engines will have a fuel filter (usually much finer than a filter on a gasoline engine), and also a water trap. The water trap (which is sometimes part of the fuel filter) often has a float connected to a warning light, which warns when there is too much water in the trap, and must be drained before damage to the engine can result. The fuel filter must be replaced much more often on a diesel engine than on a gasoline engine, changing the fuel filter every 2-4 oil changes is not uncommon for some vehicles.
Safety
Diesel fuel has low flammability, leading to a low risk of fire caused by fuel in a vehicle equipped with a diesel engine.Yachts
In yachts diesels are used because petrol engines generate combustible vapors, which can accumulate in the bottom of the vessel, sometimes causing explosions. Therefore ventilation systems on petrol powered vessels are required
Military vehicle safety
The United States Army and NATO use only diesel fuel engines and turbines because of fire hazard. Diesel does not explode in a manner such as gasoline does, it just slowly burns. US Army gasoline-engined tanks during World War II were nicknamed Ronsons, because it only took a single spark to ignite 50 or more gallons of highly volatile gasoline.
Diesel applications
Passenger cars
Diesel engines have long been popular in bigger cars and this is spreading to smaller cars. Diesel engines tend to be more economical at regular driving speeds and are much better at city speeds and at tick-over. Their reliability and life-span tend to be better (as detailed). Some 40% or more of all cars sold in Europe are diesel-powered where they are considered a low CO2 option. (However, particulate emission can be a concern). European governments traditionally favoured diesel engines in taxation policy, but this may be changing, and diesel is currently more expensive than petrol in the UK.
Diesel cars cannot accelerate as quickly as petrol cars and the increased weight of their engines (normally at the front) tends to increase tyre wear. Cold-starting is more problematical in colder climates, and in cases of difficulty they are more difficult to jump start and to bump start.
Mercedes-Benz in conjunction with Robert Bosch GmbH produced diesel-powered passenger cars starting in 1936 and very large numbers are used all over the world (often as "Grande Taxi"s in the Third World). They have put the emphasis on high performance diesel cars in their newer ranges, as does Volkswagen across various brands. Other manufacturers (Borgward in 1952, Fiat in 1953 and Peugeot in 1958) joined in, a trend which increased further in the 1970s and 1980s. Citroën sells more cars with diesel engines than gasoline engines, Peugeot) pioneered smoke-less HDI designs with filters. The Italian marque Alfa Romeo, known for design and successful history in racing, is now focusing on diesels that can be and are raced.
Turbodiesels can outperform their naturally aspirated petrol-powered sister cars. One anecdote tells of Formula One driver Jenson Button, who was arrested while driving a diesel-powered BMW 330cd Coupé at 230 km/h (about 140 mph) in France, where he was too young to have a gasoline-engined car hired to him. Button dryly observed in subsequent interviews that he had actually done BMW a public relations service, as nobody had believed a diesel road car could be driven that fast. Yet, BMW had already won the 24 Hours Nürburgring overall in 1998 with a 3-series diesel. The BMW diesel lab in Steyr, Austria is led by Ferenc Anisits and develops innovative diesel engines.
In the United States, diesel is not as popular in passenger cars as in Europe. Such cars have been traditionally perceived as heavier, noisier, having performance characteristics which make them slower to accelerate, sootier, smellier, and of being more expensive than equivalent gasoline vehicles. From the late seventies to the mid-eighties, General Motors' Oldsmobile, Cadillac, and Chevrolet divisions produced a low-powered and unreliable V8 diesel engine which generally serves as the prime example for this reputation. (The engine was a modified gasoline V8 with specialized heads rather than a completely new design.) Dodge with its ever-famous Cummins inline-six diesels optioned in pickup trucks (since about the late 1980s) really revitalized the appeal for diesel power in light vehicles among American consumers, but a superior and widely-accepted American regular-production diesel passenger car never materialized. Ford Motor Company tried diesel engines in some passenger cars in the 1980s, but to not much avail. In addition, before the introduction of 15 parts per million ultra-low sulfur diesel, which started at 15 October 2006 in the U.S. (1 June 2006 in Canada), diesel fuel used in North America still had higher sulfur content than the fuel used in Europe, effectively limiting diesel use to industrial vehicles, which had further contributed to the negative image. Ultra-low sulfur diesel is not mandatory until 2010 in the US. This image does not reflect recent designs, especially where the very high low-rev torque of modern diesels is concerned—which have characteristics similar to the big V8 gasoline engines popular in the US. Light and heavy trucks, in the U.S., have been diesel-optioned for years. After the introduction of ultra-low sulfur diesel, Mercedes-Benz has marketed passenger vehicles under the BlueTec banner. In addition, other manufacturers such as Ford, General Motors, Honda, Subaru, Audi, Volkswagen, BMW, and Nissan plan to sell Diesel vehicles in the US in 2008-2010, designed to meet the tougher emissions requirements in 2010. Recently, in early 2008, Honda has stated that they plan to offer their 50 state compliant 2.2 liter i-DTEC diesel engine in the new 2009 Acura TSX for the US market.
In Canada, Smart Fortwo was first introduced in 2004 with a diesel engine, up until 2008.
In Japan, newly registered Diesel vehicles were less than 1% in 2005. Honda and Mercedes-Benz have made plans to offer Diesel vehicles in the future, with Mercedes-Benz having already started selling the Mercedes-Benz E320 CDI in autumn 2005.Other transport uses
Larger transport applications (trucks, buses etc.) also benefit from the diesel's reliability and high torque output. Diesel displaced paraffin (or "Tractor vaporising oil", TVO) in most parts of the world by the end of the 1950s with the U.S. following some 20 years later.
In merchant ships and boats the same advantages apply, with the relative safety of diesel fuel an additional benefit. The German "pocket battleships" were the largest diesel warships, but the German torpedo-boats known as E-boats (Schnellboot) of the Second World War were also diesel craft. Conventional submarines have used them since before the First World War. American World War II diesel-electric submarines operated on two-stroke cycle as opposed to the four-stroke cycle that other navies used.
Military fuel standardisation
NATO has a single vehicle fuel policy and has selected diesel for this purpose. NATO and the United States Marine Corps have even been developing a diesel military motorcycle based on a Kawasaki off road motorcycle, with a purpose designed naturally aspirated direct injection diesel at Cranfield University in England, to be produced in the USA, because motorcycles were the last remaining petrol/gasoline powered vehicle in their inventory. Previous to this, a few civilian motorcycles had been built using adapted stationary diesel engines, but the weight and cost disadvantages generally outweighed the efficiency gains.
Engine speeds
Within the diesel engine industry, engines are often categorized by their rotational speeds into three unofficial groups:
High speed engines, medium speed engines and slow speed engines
High and medium speed engines are predominantly four stroke engines. Medium speed engines are physically larger than high speed engines and can burn lower grade (slower burning) fuel than high speed engines. Slow speed engines are predominantly large two stroke crosshead engines, hence very different from high and medium speed engines. Due to the lower rotational speed of slow and medium speed engines, there is more time for combustion during the power stroke of the cycle, and these engine are capable of utilising lower fuel grades (slower burning) fuels than high speed engines.
High-speed engines
High-speed (approximately 1000 rpm and greater) engines are used to power trucks (lorries), buses, tractors, cars, yachts, compressors, pumps and small electrical generators. As of 2008[update] most high-speed engines have indirect injection, although many modern engines, particularly in on-highway applicatons, have common rail direct injection, which is not as reliable as mechanical injection, but is cleaner burning.
Medium-speed engines
Medium speed engines are used in large electrical generators, ship propulsion and mechanical drive applications such as large compressors or pumps.
Engines used in electrical generators run at approximately 300 to 1000 rpm and are optimized to run at a set synchronous speed depending on the generation frequency (50 or 60 Hertz) and provide a rapid response to load changes. Typical synchronous speeds for modern medium speed engines are 500/514 RPM (50/60 Hz), 600 RPM (both 50 and 60 Hz), 720/750 rpm, and 900/1000 rpm.
As of 2009[update] the largest medium speed engines in current production have outputs up to approximately 20,000 kW (26,800 bhp). and are supplied by companies like MAN B&W, Wartsila,
and Rolls-Royce (acquired Ulstein Bergen Diesel in 1999). Medium speed engines produced are four-stroke machines and two-stroke units.
Typical cylinder bore size for medium speed engines ranges from 20 cm to 50 cm, and engine configurations typically are offered ranging from in-line 4 cylinder units to Vee 20 cylinder units.
Most larger medium speed engines are started with compressed air direct on pistons, using an air distributor, as opposed to a pneumatic starting motor acting on the flywheel, which tends to be used for smaller engines. There is no definitive engine size cut-off point for this.
Medium speed diesel engines operate on either diesel fuel or heavy fuel oil by direct injection in the same manner noted below for low speed engines.
It should also be noted that most major manufacturers of medium speed engines make natural gas fueled versions of their diesel cycle engines, which in fact operate on the Otto cycle, and require spark ignition, typically provided with a spark plug.
There are also dual (diesel/natural gas/coal gas) fuel versions of medium and low speed diesel engines using a lean fuel air mixture and a small injection of diesel fuel (so called "pilot fuel") for ignition. In case of a gas supply failure or maximum power demand these engines will instantly switch back to full diesel fuel operation .
Low-speed engines
Also known as "slow-speed" or traditionally "oil engines", the largest diesel engines are primarily used to power ships, although there are a few land-based power generation units as well. These extremely large two-stroke engines have power outputs up to approximately 85 MW, operate in the range from approximately 60 to 200 rpm and are up to 15.25m (50ft) tall, and can weigh over 2000 tons. They typically use direct injection running on cheap low-grade "heavy fuel", also known as "Bunker C" fuel, which requires heating in the ship for tanking and before injection due to the fuel's high viscosity. The heat for fuel heating is often provided by waste heat recovery boilers located in the exhaust ducting of the engine, which produce the steam required for fuel heating. Provided the heavy fuel system is kept warm and circulating, engines can be started and stopped on heavy fuel.
Large and medium marine engines are started with compressed air directly applied to the pistons. Air is applied to cylinders to start the engine forwards or backwards because they are normally directly connected to the propeller without clutch or gearbox, and to provide reverse propulsion either the engine must be run backwards or the ship will utilise an adjustable propeller. At least three cylinders are required with two-stroke engines and at least six cylinders with four-stroke engines to provide torque every 120 degrees.
Companies such as MAN B&W Diesel, (formerly Burmeister & Wain) and Wärtsilä (which acquired Sulzer Diesel) design such large low speed engines. They are unusually narrow and tall due to the addition of a crosshead bearing. Today (2007), the 14 cylinder Wärtsilä-Sulzer 14RTFLEX96-C turbocharged two-stroke diesel engine built by Wärtsilä licensee Doosan in Korea is the most powerful diesel engine put into service, with a cylinder bore of 960 mm (37.8 in) delivering 84.42 MW (114,800 bhp). It was put into service in September 2006, aboard the world's largest container ship Emma Maersk which belongs to the A.P. Moller-Maersk Group. Typical bore size for low speed engines ranges from approximately 35 to 98 cm (14 to 39 in). As of 2008[update], all produced low speed engines with crosshead bearings are in-line configurations; no Vee versions have been produced.
Supercharging and turbocharging
Most diesels are now turbocharged and some are both turbo charged and supercharged. Because diesels do not have fuel in the cylinder before combustion is initiated, more than one bar of air can be loaded in the cylinder without preignition. A turbocharged engine can produce significantly more power than a naturally aspirated engine of the same configuration, as having more air in the cylinders allows more fuel to be burned and thus more power to be produced. A supercharger is powered mechanically by the engine's crankshaft, while a turbocharger is powered by the engine exhaust, not requiring any mechanical power, hence turbocharging does not adversely affect the fuel economy
A two-stroke engine does not have an exhaust and intake stroke. These are performed when the piston is at the bottom of the cylinder. Therefore large two-stroke engines have a piston pump, or electrical driven turbo at startup. Smaller two stroke engines (example Detroit 71 series) are fitted with turbochargers and a mechanically driven supercharger (i.e. a Roots blower). Because turbocharged or supercharged engines produce more power for a given engine size as compared to naturally aspirated engines, attention must be paid to the mechanical design of components, lubrication, and cooling to handle the power. Pistons are usually cooled with lubrication oil sprayed on the bottom of the piston . Large diesels may use water, sea water or oil supplied through telescoping pipes attached to the cross head.